Understanding Automated Actions¶
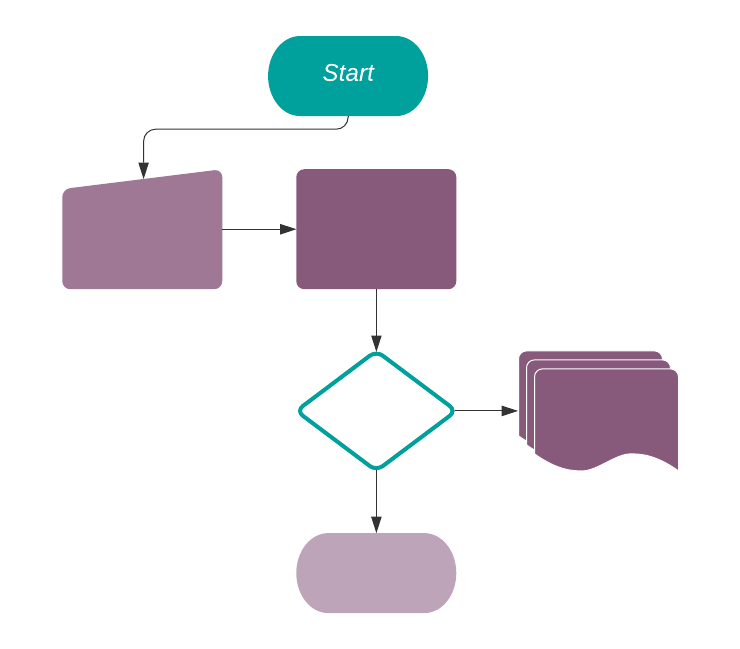
On Creation: when a new record is created. Note that the record is created once saved for the first time.
On Update: when the record is updated. Note that the update happens once the record is saved.
On Creation & Update: on the creation and/or on the update of a record once the form is saved.
On Deletion: on the removal of a record under the condition set.
Based on Form Modification: when the value of the specified Trigger field is changed in the interface (user sees the changes before saving the record). Note that this action can only be used with the Execute Python Code action type.
Based on Timed Condition: a delay happens after a specific date/time. Set a Delay after trigger date if you need a delay to happen before the Trigger Date. Example: to send a reminder 15min before a meeting. If the date/time is not set on the form of the model chosen, the date/time considered is the one of the creation/update of the record.
For every Trigger option, conditions can be applied, such as:
Before Update Domain: if designated, this condition must be satisfied before the record is updated.
Apply on: if designated, this condition must be satisfied before executing the action rule (Action To Do), and after the update.
Execute Python Code: a block of code is executed. A Help tab with the variables that can be used is available.
Create New Record: a new record with new values is created.
Update a Record: updates the record that triggered the action.
Execute several actions: defines an action that triggers other server actions.
Send Email: an automatic email is sent.
Add Followers: followers are notified of changes in the task.
Create Next Activity: creates an activity such as: Call, Email, Reminder.
Send SMS Text Message: sends an SMS.
Exemple¶
This is the process of which the update of the Email field on the Lead/Opportunity Model, with a Trigger Condition set to On Update, goes through:
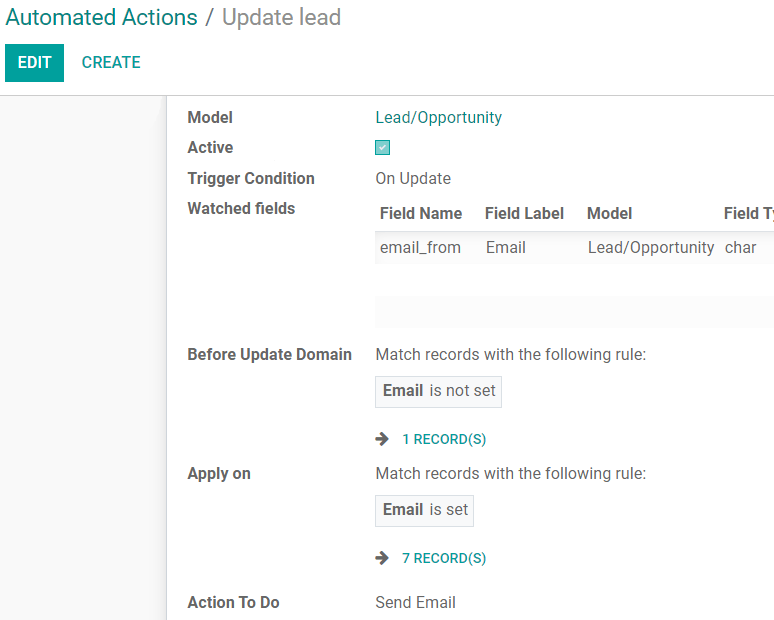
The user creates the record without an email address set.
The user updates the record defining an email address.
Once the change is saved, the automation checks if any of the Watched Fields are being updated (for the example: field name email_from (Email).
If true, it checks if the record matches the Before Update Domain (for the example: email is not set).
If true, it checks (after the update) whether the record matches the Apply on domain (for the example: email is set).
If true, the chosen Action To Do is performed on the record.
Pour plus d'infos