ORM API¶
Recordsets¶
New in version 8.0: This page documents the New API added in Odoo 8.0 which should be the primary development API going forward. It also provides information about porting from or bridging with the “old API” of versions 7 and earlier, but does not explicitly document that API. See the old documentation for that.
Interaction with models and records is performed through recordsets, a sorted set of records of the same model.
Warning
contrary to what the name implies, it is currently possible for recordsets to contain duplicates. This may change in the future.
Methods defined on a model are executed on a recordset, and their self is
a recordset:
class AModel(models.Model):
_name = 'a.model'
def a_method(self):
# self can be anywhere between 0 records and all records in the
# database
self.do_operation()
Iterating on a recordset will yield new sets of a single record (“singletons”), much like iterating on a Python string yields strings of a single characters:
def do_operation(self):
print self # => a.model(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
for record in self:
print record # => a.model(1), then a.model(2), then a.model(3), ...
Field access¶
Recordsets provide an “Active Record” interface: model fields can be read and
written directly from the record as attributes, but only on singletons
(single-record recordsets).
Field values can also be accessed like dict items, which is more elegant and
safer than getattr() for dynamic field names.
Setting a field’s value triggers an update to the database:
>>> record.name
Example Name
>>> record.company_id.name
Company Name
>>> record.name = "Bob"
>>> field = "name"
>>> record[field]
Bob
Trying to read or write a field on multiple records will raise an error.
Accessing a relational field (Many2one,
One2many, Many2many)
always returns a recordset, empty if the field is not set.
Danger
each assignment to a field triggers a database update, when setting
multiple fields at the same time or setting fields on multiple records
(to the same value), use write():
# 3 * len(records) database updates
for record in records:
record.a = 1
record.b = 2
record.c = 3
# len(records) database updates
for record in records:
record.write({'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3})
# 1 database update
records.write({'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3})
Record cache and prefetching¶
Odoo maintains a cache for the fields of the records, so that not every field access issues a database request, which would be terrible for performance. The following example queries the database only for the first statement:
record.name # first access reads value from database
record.name # second access gets value from cache
To avoid reading one field on one record at a time, Odoo prefetches records and fields following some heuristics to get good performance. Once a field must be read on a given record, the ORM actually reads that field on a larger recordset, and stores the returned values in cache for later use. The prefetched recordset is usually the recordset from which the record comes by iteration. Moreover, all simple stored fields (boolean, integer, float, char, text, date, datetime, selection, many2one) are fetched altogether; they correspond to the columns of the model’s table, and are fetched efficiently in the same query.
Consider the following example, where partners is a recordset of 1000
records. Without prefetching, the loop would make 2000 queries to the database.
With prefetching, only one query is made:
for partner in partners:
print partner.name # first pass prefetches 'name' and 'lang'
# (and other fields) on all 'partners'
print partner.lang
The prefetching also works on secondary records: when relational fields are read, their values (which are records) are subscribed for future prefetching. Accessing one of those secondary records prefetches all secondary records from the same model. This makes the following example generate only two queries, one for partners and one for countries:
countries = set()
for partner in partners:
country = partner.country_id # first pass prefetches all partners
countries.add(country.name) # first pass prefetches all countries
Set operations¶
Recordsets are immutable, but sets of the same model can be combined using various set operations, returning new recordsets. Set operations do not preserve order.
record in setreturns whetherrecord(which must be a 1-element recordset) is present inset.record not in setis the inverse operationset1 <= set2andset1 < set2return whetherset1is a subset ofset2(resp. strict)set1 >= set2andset1 > set2return whetherset1is a superset ofset2(resp. strict)set1 | set2returns the union of the two recordsets, a new recordset containing all records present in either sourceset1 & set2returns the intersection of two recordsets, a new recordset containing only records present in both sourcesset1 - set2returns a new recordset containing only records ofset1which are not inset2
Other recordset operations¶
Recordsets are iterable so the usual Python tools are available for
transformation (map(), sorted(),
itertools.ifilter, …) however these return either a
list or an iterator, removing the ability to
call methods on their result, or to use set operations.
Recordsets therefore provide these operations returning recordsets themselves (when possible):
filtered()returns a recordset containing only records satisfying the provided predicate function. The predicate can also be a string to filter by a field being true or false:
# only keep records whose company is the current user's records.filtered(lambda r: r.company_id == user.company_id) # only keep records whose partner is a company records.filtered("partner_id.is_company")
sorted()returns a recordset sorted by the provided key function. If no key is provided, use the model’s default sort order:
# sort records by name records.sorted(key=lambda r: r.name)
mapped()applies the provided function to each record in the recordset, returns a recordset if the results are recordsets:
# returns a list of summing two fields for each record in the set records.mapped(lambda r: r.field1 + r.field2)
The provided function can be a string to get field values:
# returns a list of names records.mapped('name') # returns a recordset of partners record.mapped('partner_id') # returns the union of all partner banks, with duplicates removed record.mapped('partner_id.bank_ids')
Environment¶
The Environment stores various contextual data used by
the ORM: the database cursor (for database queries), the current user
(for access rights checking) and the current context (storing arbitrary
metadata). The environment also stores caches.
All recordsets have an environment, which is immutable, can be accessed
using env and gives access to the current user
(user), the cursor
(cr) or the context
(context):
>>> records.env
<Environment object ...>
>>> records.env.user
res.user(3)
>>> records.env.cr
<Cursor object ...)
When creating a recordset from an other recordset, the environment is inherited. The environment can be used to get an empty recordset in an other model, and query that model:
>>> self.env['res.partner']
res.partner
>>> self.env['res.partner'].search([['is_company', '=', True], ['customer', '=', True]])
res.partner(7, 18, 12, 14, 17, 19, 8, 31, 26, 16, 13, 20, 30, 22, 29, 15, 23, 28, 74)
Altering the environment¶
The environment can be customized from a recordset. This returns a new version of the recordset using the altered environment.
sudo()creates a new environment with the provided user set, uses the administrator if none is provided (to bypass access rights/rules in safe contexts), returns a copy of the recordset it is called on using the new environment:
# create partner object as administrator env['res.partner'].sudo().create({'name': "A Partner"}) # list partners visible by the "public" user public = env.ref('base.public_user') env['res.partner'].sudo(public).search([])
with_context()can take a single positional parameter, which replaces the current environment’s context
can take any number of parameters by keyword, which are added to either the current environment’s context or the context set during step 1
# look for partner, or create one with specified timezone if none is # found env['res.partner'].with_context(tz=a_tz).find_or_create(email_address)
with_env()replaces the existing environment entirely
Common ORM methods¶
search()Takes a search domain, returns a recordset of matching records. Can return a subset of matching records (
offsetandlimitparameters) and be ordered (orderparameter):>>> # searches the current model >>> self.search([('is_company', '=', True), ('customer', '=', True)]) res.partner(7, 18, 12, 14, 17, 19, 8, 31, 26, 16, 13, 20, 30, 22, 29, 15, 23, 28, 74) >>> self.search([('is_company', '=', True)], limit=1).name 'Agrolait'
Tip
to just check if any record matches a domain, or count the number of records which do, use
search_count()create()Takes a dictionary of field values, or a list of such dictionaries, and returns a recordset containing the records created:
>>> self.create({'name': "Joe"}) res.partner(78) >>> self.create([{'name': "Jack"}, {'name': "William"}, {'name': "Averell"}]) res.partner(79, 80, 81)
See how to define method `create` with one API or the other.
write()Takes a number of field values, writes them to all the records in its recordset. Does not return anything:
self.write({'name': "Newer Name"})
browse()Takes a database id or a list of ids and returns a recordset, useful when record ids are obtained from outside Odoo (e.g. round-trip through external system) or when calling methods in the old API:
>>> self.browse([7, 18, 12]) res.partner(7, 18, 12)
exists()Returns a new recordset containing only the records which exist in the database. Can be used to check whether a record (e.g. obtained externally) still exists:
if not record.exists(): raise Exception("The record has been deleted")
or after calling a method which could have removed some records:
records.may_remove_some() # only keep records which were not deleted records = records.exists()
ref()Environment method returning the record matching a provided external id:
>>> env.ref('base.group_public') res.groups(2)
ensure_one()checks that the recordset is a singleton (only contains a single record), raises an error otherwise:
records.ensure_one() # is equivalent to but clearer than: assert len(records) == 1, "Expected singleton"
Creating Models¶
Model fields are defined as attributes on the model itself:
from odoo import models, fields
class AModel(models.Model):
_name = 'a.model.name'
field1 = fields.Char()
Warning
this means you can not define a field and a method with the same name, they will conflict
By default, the field’s label (user-visible name) is a capitalized version of
the field name, this can be overridden with the string parameter:
field2 = fields.Integer(string="an other field")
For the various field types and parameters, see the fields reference.
Default values are defined as parameters on fields, either a value:
a_field = fields.Char(default="a value")
or a function called to compute the default value, which should return that value:
def compute_default_value(self):
return self.get_value()
a_field = fields.Char(default=compute_default_value)
Computed fields¶
Fields can be computed (instead of read straight from the database) using the
compute parameter. It must assign the computed value to the field. If
it uses the values of other fields, it should specify those fields using
depends():
from odoo import api
total = fields.Float(compute='_compute_total')
@api.depends('value', 'tax')
def _compute_total(self):
for record in self:
record.total = record.value + record.value * record.tax
dependencies can be dotted paths when using sub-fields:
@api.depends('line_ids.value') def _compute_total(self): for record in self: record.total = sum(line.value for line in record.line_ids)
computed fields are not stored by default, they are computed and returned when requested. Setting
store=Truewill store them in the database and automatically enable searchingsearching on a computed field can also be enabled by setting the
searchparameter. The value is a method name returning a Domains:upper_name = field.Char(compute='_compute_upper', search='_search_upper') def _search_upper(self, operator, value): if operator == 'like': operator = 'ilike' return [('name', operator, value)]
to allow setting values on a computed field, use the
inverseparameter. It is the name of a function reversing the computation and setting the relevant fields:document = fields.Char(compute='_get_document', inverse='_set_document') def _get_document(self): for record in self: with open(record.get_document_path) as f: record.document = f.read() def _set_document(self): for record in self: if not record.document: continue with open(record.get_document_path()) as f: f.write(record.document)
multiple fields can be computed at the same time by the same method, just use the same method on all fields and set all of them:
discount_value = fields.Float(compute='_apply_discount') total = fields.Float(compute='_apply_discount') @depends('value', 'discount') def _apply_discount(self): for record in self: # compute actual discount from discount percentage discount = record.value * record.discount record.discount_value = discount record.total = record.value - discount
onchange: updating UI on the fly¶
When a user changes a field’s value in a form (but hasn’t saved the form yet), it can be useful to automatically update other fields based on that value e.g. updating a final total when the tax is changed or a new invoice line is added.
computed fields are automatically checked and recomputed, they do not need an
onchangefor non-computed fields, the
onchange()decorator is used to provide new field values:@api.onchange('field1', 'field2') # if these fields are changed, call method def check_change(self): if self.field1 < self.field2: self.field3 = True
the changes performed during the method are then sent to the client program and become visible to the user
Both computed fields and new-API onchanges are automatically called by the client without having to add them in views
It is possible to suppress the trigger from a specific field by adding
on_change="0"in a view:<field name="name" on_change="0"/>
will not trigger any interface update when the field is edited by the user, even if there are function fields or explicit onchange depending on that field.
Note
onchange methods work on virtual records assignment on these records
is not written to the database, just used to know which value to send back
to the client
Warning
It is not possible for a one2many or many2many field to modify
itself via onchange. This is a webclient limitation - see #2693.
Low-level SQL¶
The cr attribute on environments is the
cursor for the current database transaction and allows executing SQL directly,
either for queries which are difficult to express using the ORM (e.g. complex
joins) or for performance reasons:
self.env.cr.execute("some_sql", params)
Because models use the same cursor and the Environment
holds various caches, these caches must be invalidated when altering the
database in raw SQL, or further uses of models may become incoherent. It is
necessary to clear caches when using CREATE, UPDATE or DELETE in
SQL, but not SELECT (which simply reads the database).
Clearing caches can be performed using the
invalidate_cache() method of the
BaseModel object.
Compatibility between new API and old API¶
Odoo is currently transitioning from an older (less regular) API, it can be necessary to manually bridge from one to the other manually:
RPC layers (both XML-RPC and JSON-RPC) are expressed in terms of the old API, methods expressed purely in the new API are not available over RPC
overridable methods may be called from older pieces of code still written in the old API style
The big differences between the old and new APIs are:
values of the
Environment(cursor, user id and context) are passed explicitly to methods insteadrecord data (
ids) are passed explicitly to methods, and possibly not passed at allmethods tend to work on lists of ids instead of recordsets
By default, methods are assumed to use the new API style and are not callable from the old API style.
Tip
calls from the new API to the old API are bridged
when using the new API style, calls to methods defined using the old API are automatically converted on-the-fly, there should be no need to do anything special:
>>> # method in the old API style
>>> def old_method(self, cr, uid, ids, context=None):
... print ids
>>> # method in the new API style
>>> def new_method(self):
... # system automatically infers how to call the old-style
... # method from the new-style method
... self.old_method()
>>> env[model].browse([1, 2, 3, 4]).new_method()
[1, 2, 3, 4]
Two decorators can expose a new-style method to the old API:
model()the method is exposed as not using ids, its recordset will generally be empty. Its “old API” signature is
cr, uid, *arguments, context:@api.model def some_method(self, a_value): pass # can be called as old_style_model.some_method(cr, uid, a_value, context=context)
multi()the method is exposed as taking a list of ids (possibly empty), its “old API” signature is
cr, uid, ids, *arguments, context:@api.multi def some_method(self, a_value): pass # can be called as old_style_model.some_method(cr, uid, [id1, id2], a_value, context=context)
Note that a method create decorated with model() will always
be called with a single dictionary. A method create decorated with the variant
model_create_multi() will always be called with a list of dicts.
The decorators take care of converting the argument to one form or the other:
@api.model
def create(self, vals):
...
@api.model_create_multi
def create(self, vals_list):
...
Because new-style APIs tend to return recordsets and old-style APIs tend to return lists of ids, there is also a decorator managing this:
returns()the function is assumed to return a recordset, the first parameter should be the name of the recordset’s model or
self(for the current model).No effect if the method is called in new API style, but transforms the recordset into a list of ids when called from the old API style:
>>> @api.multi ... @api.returns('self') ... def some_method(self): ... return self >>> new_style_model = env['a.model'].browse(1, 2, 3) >>> new_style_model.some_method() a.model(1, 2, 3) >>> old_style_model = pool['a.model'] >>> old_style_model.some_method(cr, uid, [1, 2, 3], context=context) [1, 2, 3]
Model Reference¶
-
class
odoo.models.Model[source]¶ Main super-class for regular database-persisted Odoo models.
Odoo models are created by inheriting from this class:
class user(Model): ...
The system will later instantiate the class once per database (on which the class’ module is installed).
Structural attributes
-
_name¶ business object name, in dot-notation (in module namespace)
-
_rec_name¶ Alternative field to use as name, used by osv’s name_get() (default:
'name')
-
_inherit¶
-
_auto¶ Whether a database table should be created (default:
True)If set to
False, overrideinit()to create the database tableTip
To create a model without any table, inherit from
odoo.models.AbstractModel
-
_inherits¶ dictionary mapping the _name of the parent business objects to the names of the corresponding foreign key fields to use:
_inherits = { 'a.model': 'a_field_id', 'b.model': 'b_field_id' }
implements composition-based inheritance: the new model exposes all the fields of the
_inherits-ed model but stores none of them: the values themselves remain stored on the linked record.Warning
if the same field is defined on multiple
_inherits-ed
-
_constraints¶ list of
(constraint_function, message, fields)defining Python constraints. The fields list is indicativeDeprecated since version 8.0: use
constrains()
-
_sql_constraints¶ list of
(name, sql_definition, message)triples defining SQL constraints to execute when generating the backing table
-
_parent_store¶ Alongside a
parent_pathfield, sets up an indexed storage of the tree structure of records, to enable faster hierarchical queries on the records of the current model using thechild_ofandparent_ofdomain operators. (default:False)- Type
-
_parent_name¶ Alternative field to use as parent, used by indexed storage of the tree structure of records (default:
'parent_id')- type
str
-
_date_name¶ Alternative field to use for default calendar view (default:
'date')- type
str
-
_fold_name¶ Alternative field to determine folded groups in kanban views (default:
'fold')- type
str
-
_translate¶ False disables translations export for this model (default:
True)- type
bool
CRUD
-
create(vals_list) → records[source]¶ Creates new records for the model.
The new records are initialized using the values from the list of dicts
vals_list, and if necessary those fromdefault_get().- Parameters
vals_list (list) –
values for the model’s fields, as a list of dictionaries:
[{'field_name': field_value, ...}, ...]
For backward compatibility,
vals_listmay be a dictionary. It is treated as a singleton list[vals], and a single record is returned.see
write()for details- Returns
the created records
- Raises
AccessError –
if user has no create rights on the requested object
if user tries to bypass access rules for create on the requested object
ValidateError – if user tries to enter invalid value for a field that is not in selection
UserError – if a loop would be created in a hierarchy of objects a result of the operation (such as setting an object as its own parent)
-
browse([ids]) → records[source]¶ Returns a recordset for the ids provided as parameter in the current environment.
Can take no ids, a single id or a sequence of ids.
-
unlink()[source]¶ Deletes the records of the current set
- Raises
AccessError –
if user has no unlink rights on the requested object
if user tries to bypass access rules for unlink on the requested object
UserError – if the record is default property for other records
-
write(vals)[source]¶ Updates all records in the current set with the provided values.
- Parameters
vals (dict) –
fields to update and the value to set on them e.g:
{'foo': 1, 'bar': "Qux"}
will set the field
footo1and the fieldbarto"Qux"if those are valid (otherwise it will trigger an error).- Raises
AccessError –
if user has no write rights on the requested object
if user tries to bypass access rules for write on the requested object
ValidateError – if user tries to enter invalid value for a field that is not in selection
UserError – if a loop would be created in a hierarchy of objects a result of the operation (such as setting an object as its own parent)
For numeric fields (
Integer,Float) the value should be of the corresponding typeFor
Selection, the value should match the selection values (generallystr, sometimesint)For
Many2one, the value should be the database identifier of the record to setOther non-relational fields use a string for value
One2manyandMany2manyuse a special “commands” format to manipulate the set of records stored in/associated with the field.This format is a list of triplets executed sequentially, where each triplet is a command to execute on the set of records. Not all commands apply in all situations. Possible commands are:
(0, _, values)adds a new record created from the provided
valuedict.(1, id, values)updates an existing record of id
idwith the values invalues. Can not be used increate().(2, id, _)removes the record of id
idfrom the set, then deletes it (from the database). Can not be used increate().(3, id, _)removes the record of id
idfrom the set, but does not delete it. Can not be used increate().(4, id, _)adds an existing record of id
idto the set.(5, _, _)removes all records from the set, equivalent to using the command
3on every record explicitly. Can not be used increate().(6, _, ids)replaces all existing records in the set by the
idslist, equivalent to using the command5followed by a command4for eachidinids.
Note
Values marked as
_in the list above are ignored and can be anything, generally0orFalse.
-
read([fields])[source]¶ Reads the requested fields for the records in
self, low-level/RPC method. In Python code, preferbrowse().- Parameters
fields – list of field names to return (default is all fields)
- Returns
a list of dictionaries mapping field names to their values, with one dictionary per record
- Raises
AccessError – if user has no read rights on some of the given records
-
read_group(domain, fields, groupby, offset=0, limit=None, orderby=False, lazy=True)[source]¶ Get the list of records in list view grouped by the given
groupbyfields- Parameters
domain – list specifying search criteria [[‘field_name’, ‘operator’, ‘value’], …]
fields (list) – list of fields present in the list view specified on the object. Each element is either ‘field’ (field name, using the default aggregation), or ‘field:agg’ (aggregate field with aggregation function ‘agg’), or ‘name:agg(field)’ (aggregate field with ‘agg’ and return it as ‘name’). The possible aggregation functions are the ones provided by PostgreSQL (https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/static/functions-aggregate.html) and ‘count_distinct’, with the expected meaning.
groupby (list) – list of groupby descriptions by which the records will be grouped. A groupby description is either a field (then it will be grouped by that field) or a string ‘field:groupby_function’. Right now, the only functions supported are ‘day’, ‘week’, ‘month’, ‘quarter’ or ‘year’, and they only make sense for date/datetime fields.
offset (int) – optional number of records to skip
limit (int) – optional max number of records to return
orderby (list) – optional
order byspecification, for overriding the natural sort ordering of the groups, see alsosearch()(supported only for many2one fields currently)lazy (bool) – if true, the results are only grouped by the first groupby and the remaining groupbys are put in the __context key. If false, all the groupbys are done in one call.
- Returns
list of dictionaries(one dictionary for each record) containing:
the values of fields grouped by the fields in
groupbyargument__domain: list of tuples specifying the search criteria
__context: dictionary with argument like
groupby
- Return type
[{‘field_name_1’: value, ..]
- Raises
AccessError –
if user has no read rights on the requested object
if user tries to bypass access rules for read on the requested object
Searching
-
search(args[, offset=0][, limit=None][, order=None][, count=False])[source]¶ Searches for records based on the
argssearch domain.- Parameters
args – A search domain. Use an empty list to match all records.
offset (int) – number of results to ignore (default: none)
limit (int) – maximum number of records to return (default: all)
order (str) – sort string
count (bool) – if True, only counts and returns the number of matching records (default: False)
- Returns
at most
limitrecords matching the search criteria- Raises
AccessError –
if user tries to bypass access rules for read on the requested object.
-
search_count(args) → int[source]¶ Returns the number of records in the current model matching the provided domain.
-
name_search(name='', args=None, operator='ilike', limit=100) → records[source]¶ Search for records that have a display name matching the given
namepattern when compared with the givenoperator, while also matching the optional search domain (args).This is used for example to provide suggestions based on a partial value for a relational field. Sometimes be seen as the inverse function of
name_get(), but it is not guaranteed to be.This method is equivalent to calling
search()with a search domain based ondisplay_nameand thenname_get()on the result of the search.- Parameters
- Return type
- Returns
list of pairs
(id, text_repr)for all matching records.
Recordset operations
-
ids¶ List of actual record ids in this recordset (ignores placeholder ids for records to create)
-
ensure_one()[source]¶ Verifies that the current recorset holds a single record. Raises an exception otherwise.
-
exists() → records[source]¶ Returns the subset of records in
selfthat exist, and marks deleted records as such in cache. It can be used as a test on records:if record.exists(): ...
By convention, new records are returned as existing.
-
filtered(func)[source]¶ Select the records in
selfsuch thatfunc(rec)is true, and return them as a recordset.- Parameters
func – a function or a dot-separated sequence of field names
-
sorted(key=None, reverse=False)[source]¶ Return the recordset
selfordered bykey.- Parameters
key – either a function of one argument that returns a comparison key for each record, or a field name, or
None, in which case records are ordered according the default model’s orderreverse – if
True, return the result in reverse order
-
mapped(func)[source]¶ Apply
funcon all records inself, and return the result as a list or a recordset (iffuncreturn recordsets). In the latter case, the order of the returned recordset is arbitrary.- Parameters
func – a function or a dot-separated sequence of field names (string); any falsy value simply returns the recordset
self
Environment swapping
-
sudo([user=SUPERUSER])[source]¶ Returns a new version of this recordset attached to the provided user.
By default this returns a
SUPERUSERrecordset, where access control and record rules are bypassed.Note
Using
sudocould cause data access to cross the boundaries of record rules, possibly mixing records that are meant to be isolated (e.g. records from different companies in multi-company environments).It may lead to un-intuitive results in methods which select one record among many - for example getting the default company, or selecting a Bill of Materials.
Note
Because the record rules and access control will have to be re-evaluated, the new recordset will not benefit from the current environment’s data cache, so later data access may incur extra delays while re-fetching from the database. The returned recordset has the same prefetch object as
self.
-
with_context([context][, **overrides]) → records[source]¶ Returns a new version of this recordset attached to an extended context.
The extended context is either the provided
contextin whichoverridesare merged or the current context in whichoverridesare merged e.g.:# current context is {'key1': True} r2 = records.with_context({}, key2=True) # -> r2._context is {'key2': True} r2 = records.with_context(key2=True) # -> r2._context is {'key1': True, 'key2': True}
-
with_env(env)[source]¶ Returns a new version of this recordset attached to the provided environment
Warning
The new environment will not benefit from the current environment’s data cache, so later data access may incur extra delays while re-fetching from the database. The returned recordset has the same prefetch object as
self.
Fields and views querying
-
fields_get([fields][, attributes])[source]¶ Return the definition of each field.
The returned value is a dictionary (indiced by field name) of dictionaries. The _inherits’d fields are included. The string, help, and selection (if present) attributes are translated.
- Parameters
allfields – list of fields to document, all if empty or not provided
attributes – list of description attributes to return for each field, all if empty or not provided
-
fields_view_get([view_id | view_type='form'])[source]¶ Get the detailed composition of the requested view like fields, model, view architecture
- Parameters
view_id – id of the view or None
view_type – type of the view to return if view_id is None (‘form’, ‘tree’, …)
toolbar – true to include contextual actions
submenu – deprecated
- Returns
dictionary describing the composition of the requested view (including inherited views and extensions)
- Raises
if the inherited view has unknown position to work with other than ‘before’, ‘after’, ‘inside’, ‘replace’
if some tag other than ‘position’ is found in parent view
Invalid ArchitectureError – if there is view type other than form, tree, calendar, search etc defined on the structure
Miscellaneous methods
-
default_get(fields) → default_values[source]¶ Return default values for the fields in
fields_list. Default values are determined by the context, user defaults, and the model itself.- Parameters
fields_list – a list of field names
- Returns
a dictionary mapping each field name to its corresponding default value, if it has one.
-
copy(default=None)[source]¶ Duplicate record
selfupdating it with default values- Parameters
default (dict) – dictionary of field values to override in the original values of the copied record, e.g:
{'field_name': overridden_value, ...}- Returns
new record
-
name_get() → [id, name, …][source]¶ Returns a textual representation for the records in
self. By default this is the value of thedisplay_namefield.
-
name_create(name) → record[source]¶ Create a new record by calling
create()with only one value provided: the display name of the new record.The new record will be initialized with any default values applicable to this model, or provided through the context. The usual behavior of
create()applies.- Parameters
name – display name of the record to create
- Return type
- Returns
the
name_get()pair value of the created record
Automatic fields
-
_log_access¶ Whether log access fields (
create_date,write_uid, …) should be generated (default:True)
-
create_date¶ Date at which the record was created
- Type
Datetime
-
create_uid¶ Relational field to the user who created the record
- Type
res.users
-
write_date¶ Date at which the record was last modified
- Type
Datetime
-
write_uid¶ Relational field to the last user who modified the record
- Type
res.users
Reserved field names
A few field names are reserved for pre-defined behaviors beyond that of automated fields. They should be defined on a model when the related behavior is desired:
-
name¶ default value for
_rec_name, used to display records in context where a representative “naming” is necessary.- Type
-
active¶ toggles the global visibility of the record, if
activeis set toFalsethe record is invisible in most searches and listing- Type
-
sequence¶ Alterable ordering criteria, allows drag-and-drop reordering of models in list views
- Type
-
parent_id¶ used to order records in a tree structure and enables the
child_ofandparent_ofoperators in domains- Type
-
parent_path¶ used to store an index of the tree structure when
_parent_storeis set to True - must be declared withindex=Truefor proper operation.- Type
-
Method decorators¶
This module provides the elements for managing two different API styles, namely the “traditional” and “record” styles.
In the “traditional” style, parameters like the database cursor, user id,
context dictionary and record ids (usually denoted as cr, uid,
context, ids) are passed explicitly to all methods. In the “record”
style, those parameters are hidden into model instances, which gives it a
more object-oriented feel.
For instance, the statements:
model = self.pool.get(MODEL)
ids = model.search(cr, uid, DOMAIN, context=context)
for rec in model.browse(cr, uid, ids, context=context):
print rec.name
model.write(cr, uid, ids, VALUES, context=context)
may also be written as:
env = Environment(cr, uid, context) # cr, uid, context wrapped in env
model = env[MODEL] # retrieve an instance of MODEL
recs = model.search(DOMAIN) # search returns a recordset
for rec in recs: # iterate over the records
print rec.name
recs.write(VALUES) # update all records in recs
Methods written in the “traditional” style are automatically decorated, following some heuristics based on parameter names.
-
odoo.api.constrains(*args)[source]¶ Decorates a constraint checker. Each argument must be a field name used in the check:
@api.one @api.constrains('name', 'description') def _check_description(self): if self.name == self.description: raise ValidationError("Fields name and description must be different")
Invoked on the records on which one of the named fields has been modified.
Should raise
ValidationErrorif the validation failed.Warning
@constrainsonly supports simple field names, dotted names (fields of relational fields e.g.partner_id.customer) are not supported and will be ignored@constrainswill be triggered only if the declared fields in the decorated method are included in thecreateorwritecall. It implies that fields not present in a view will not trigger a call during a record creation. A override ofcreateis necessary to make sure a constraint will always be triggered (e.g. to test the absence of value).
-
odoo.api.depends(*args)[source]¶ Return a decorator that specifies the field dependencies of a “compute” method (for new-style function fields). Each argument must be a string that consists in a dot-separated sequence of field names:
pname = fields.Char(compute='_compute_pname') @api.one @api.depends('partner_id.name', 'partner_id.is_company') def _compute_pname(self): if self.partner_id.is_company: self.pname = (self.partner_id.name or "").upper() else: self.pname = self.partner_id.name
One may also pass a single function as argument. In that case, the dependencies are given by calling the function with the field’s model.
-
odoo.api.model(method)[source]¶ Decorate a record-style method where
selfis a recordset, but its contents is not relevant, only the model is. Such a method:@api.model def method(self, args): ...
may be called in both record and traditional styles, like:
# recs = model.browse(cr, uid, ids, context) recs.method(args) model.method(cr, uid, args, context=context)
Notice that no
idsare passed to the method in the traditional style.
-
odoo.api.multi(method)[source]¶ Decorate a record-style method where
selfis a recordset. The method typically defines an operation on records. Such a method:@api.multi def method(self, args): ...
may be called in both record and traditional styles, like:
# recs = model.browse(cr, uid, ids, context) recs.method(args) model.method(cr, uid, ids, args, context=context)
-
odoo.api.onchange(*args)[source]¶ Return a decorator to decorate an onchange method for given fields. Each argument must be a field name:
@api.onchange('partner_id') def _onchange_partner(self): self.message = "Dear %s" % (self.partner_id.name or "")
In the form views where the field appears, the method will be called when one of the given fields is modified. The method is invoked on a pseudo-record that contains the values present in the form. Field assignments on that record are automatically sent back to the client.
The method may return a dictionary for changing field domains and pop up a warning message, like in the old API:
return { 'domain': {'other_id': [('partner_id', '=', partner_id)]}, 'warning': {'title': "Warning", 'message': "What is this?"}, }
Danger
Since
@onchangereturns a recordset of pseudo-records, calling any one of the CRUD methods (create(),read(),write(),unlink()) on the aforementioned recordset is undefined behaviour, as they potentially do not exist in the database yet.Instead, simply set the record’s field like shown in the example above or call the
update()method.Warning
@onchangeonly supports simple field names, dotted names (fields of relational fields e.g.partner_id.tz) are not supported and will be ignored
-
odoo.api.one(method)[source]¶ Decorate a record-style method where
selfis expected to be a singleton instance. The decorated method automatically loops on records, and makes a list with the results. In case the method is decorated withreturns(), it concatenates the resulting instances. Such a method:@api.one def method(self, args): return self.name
may be called in both record and traditional styles, like:
# recs = model.browse(cr, uid, ids, context) names = recs.method(args) names = model.method(cr, uid, ids, args, context=context)
Deprecated since version 9.0:
one()often makes the code less clear and behaves in ways developers and readers may not expect.It is strongly recommended to use
multi()and either iterate on theselfrecordset or ensure that the recordset is a single record withensure_one().
-
odoo.api.returns(model, downgrade=None, upgrade=None)[source]¶ Return a decorator for methods that return instances of
model.- Parameters
model – a model name, or
'self'for the current modeldowngrade – a function
downgrade(self, value, *args, **kwargs)to convert the record-stylevalueto a traditional-style outputupgrade – a function
upgrade(self, value, *args, **kwargs)to convert the traditional-stylevalueto a record-style output
The arguments
self,*argsand**kwargsare the ones passed to the method in the record-style.The decorator adapts the method output to the api style:
id,idsorFalsefor the traditional style, and recordset for the record style:@model @returns('res.partner') def find_partner(self, arg): ... # return some record # output depends on call style: traditional vs record style partner_id = model.find_partner(cr, uid, arg, context=context) # recs = model.browse(cr, uid, ids, context) partner_record = recs.find_partner(arg)
Note that the decorated method must satisfy that convention.
Those decorators are automatically inherited: a method that overrides a decorated existing method will be decorated with the same
@returns(model).
-
odoo.api.v7(method_v7)[source]¶ Decorate a method that supports the old-style api only. A new-style api may be provided by redefining a method with the same name and decorated with
v8():@api.v7 def foo(self, cr, uid, ids, context=None): ... @api.v8 def foo(self): ...
Special care must be taken if one method calls the other one, because the method may be overridden! In that case, one should call the method from the current class (say
MyClass), for instance:@api.v7 def foo(self, cr, uid, ids, context=None): # Beware: records.foo() may call an overriding of foo() records = self.browse(cr, uid, ids, context) return MyClass.foo(records)
Note that the wrapper method uses the docstring of the first method.
-
odoo.api.v8(method_v8)[source]¶ Decorate a method that supports the new-style api only. An old-style api may be provided by redefining a method with the same name and decorated with
v7():@api.v8 def foo(self): ... @api.v7 def foo(self, cr, uid, ids, context=None): ...
Note that the wrapper method uses the docstring of the first method.
Fields¶
Basic fields¶
-
class
odoo.fields.Field(string=<object object>, **kwargs)[source]¶ The field descriptor contains the field definition, and manages accesses and assignments of the corresponding field on records. The following attributes may be provided when instanciating a field:
- Parameters
string – the label of the field seen by users (string); if not set, the ORM takes the field name in the class (capitalized).
help – the tooltip of the field seen by users (string)
readonly – whether the field is readonly (boolean, by default
False)required – whether the value of the field is required (boolean, by default
False)index – whether the field is indexed in database. Note: no effect on non-stored and virtual fields. (boolean, by default
False)default – the default value for the field; this is either a static value, or a function taking a recordset and returning a value; use
default=Noneto discard default values for the fieldstates – a dictionary mapping state values to lists of UI attribute-value pairs; possible attributes are: ‘readonly’, ‘required’, ‘invisible’. Note: Any state-based condition requires the
statefield value to be available on the client-side UI. This is typically done by including it in the relevant views, possibly made invisible if not relevant for the end-user.groups – comma-separated list of group xml ids (string); this restricts the field access to the users of the given groups only
copy (bool) – whether the field value should be copied when the record is duplicated (default:
Truefor normal fields,Falseforone2manyand computed fields, including property fields and related fields)oldname (str) – the previous name of this field, so that ORM can rename it automatically at migration
group_operator (str) –
aggregate function used by
read_group()when grouping on this field.Supported aggregate functions are:
array_agg: values, including nulls, concatenated into an arraycount: number of rowscount_distinct: number of distinct rowsbool_and: true if all values are true, otherwise falsebool_or: true if at least one value is true, otherwise falsemax: maximum value of all valuesmin: minimum value of all valuesavg: the average (arithmetic mean) of all valuessum: sum of all values
Computed fields
One can define a field whose value is computed instead of simply being read from the database. The attributes that are specific to computed fields are given below. To define such a field, simply provide a value for the attribute
compute.- Parameters
compute – name of a method that computes the field
inverse – name of a method that inverses the field (optional)
search – name of a method that implement search on the field (optional)
store – whether the field is stored in database (boolean, by default
Falseon computed fields)compute_sudo – whether the field should be recomputed as superuser to bypass access rights (boolean, by default
False) Note that this has no effects on non-stored computed fields
The methods given for
compute,inverseandsearchare model methods. Their signature is shown in the following example:upper = fields.Char(compute='_compute_upper', inverse='_inverse_upper', search='_search_upper') @api.depends('name') def _compute_upper(self): for rec in self: rec.upper = rec.name.upper() if rec.name else False def _inverse_upper(self): for rec in self: rec.name = rec.upper.lower() if rec.upper else False def _search_upper(self, operator, value): if operator == 'like': operator = 'ilike' return [('name', operator, value)]
The compute method has to assign the field on all records of the invoked recordset. The decorator
odoo.api.depends()must be applied on the compute method to specify the field dependencies; those dependencies are used to determine when to recompute the field; recomputation is automatic and guarantees cache/database consistency. Note that the same method can be used for several fields, you simply have to assign all the given fields in the method; the method will be invoked once for all those fields.By default, a computed field is not stored to the database, and is computed on-the-fly. Adding the attribute
store=Truewill store the field’s values in the database. The advantage of a stored field is that searching on that field is done by the database itself. The disadvantage is that it requires database updates when the field must be recomputed.The inverse method, as its name says, does the inverse of the compute method: the invoked records have a value for the field, and you must apply the necessary changes on the field dependencies such that the computation gives the expected value. Note that a computed field without an inverse method is readonly by default.
Warning
While it is possible to use the same compute method for multiple fields, it is not recommended to do the same for the inverse method.
During the computation of the inverse, all fields that use said inverse are protected, meaning that they can’t be computed, even if their value is not in the cache.
If any of those fields is accessed and its value is not in cache, the ORM will simply return a default value of
Falsefor these fields. This means that the value of the inverse fields (other than the one triggering the inverse method) may not give their correct value and this will probably break the expected behavior of the inverse method.The search method is invoked when processing domains before doing an actual search on the model. It must return a domain equivalent to the condition:
field operator value.The value of a related field is given by following a sequence of relational fields and reading a field on the reached model. The complete sequence of fields to traverse is specified by the attribute
- Parameters
related – sequence of field names
Some field attributes are automatically copied from the source field if they are not redefined:
string,help,readonly,required(only if all fields in the sequence are required),groups,digits,size,translate,sanitize,selection,comodel_name,domain,context. All semantic-free attributes are copied from the source field.By default, the values of related fields are not stored to the database. Add the attribute
store=Trueto make it stored, just like computed fields. Related fields are automatically recomputed when their dependencies are modified.Company-dependent fields
Formerly known as ‘property’ fields, the value of those fields depends on the company. In other words, users that belong to different companies may see different values for the field on a given record.
Warning
Company-dependent fields aren’t stored in the table of the model they’re defined on, instead, they are stored in the
ir.propertymodel’s table.- Parameters
company_dependent – whether the field is company-dependent (boolean)
Incremental definition
A field is defined as class attribute on a model class. If the model is extended (see
Model), one can also extend the field definition by redefining a field with the same name and same type on the subclass. In that case, the attributes of the field are taken from the parent class and overridden by the ones given in subclasses.For instance, the second class below only adds a tooltip on the field
state:class First(models.Model): _name = 'foo' state = fields.Selection([...], required=True) class Second(models.Model): _inherit = 'foo' state = fields.Selection(help="Blah blah blah")
-
class
odoo.fields.Char(string=<object object>, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
odoo.fields._StringBasic string field, can be length-limited, usually displayed as a single-line string in clients.
- Parameters
size (int) – the maximum size of values stored for that field
trim (bool) – states whether the value is trimmed or not (by default,
True). Note that the trim operation is applied only by the web client.translate – enable the translation of the field’s values; use
translate=Trueto translate field values as a whole;translatemay also be a callable such thattranslate(callback, value)translatesvalueby usingcallback(term)to retrieve the translation of terms.
-
class
odoo.fields.Boolean(string=<object object>, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
odoo.fields.Field
-
class
odoo.fields.Integer(string=<object object>, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
odoo.fields.Field
-
class
odoo.fields.Float(string=<object object>, digits=<object object>, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
odoo.fields.FieldThe precision digits are given by the attribute
- Parameters
digits – a pair (total, decimal), or a function taking a database cursor and returning a pair (total, decimal)
-
class
odoo.fields.Text(string=<object object>, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
odoo.fields._StringVery similar to
Charbut used for longer contents, does not have a size and usually displayed as a multiline text box.- Parameters
translate – enable the translation of the field’s values; use
translate=Trueto translate field values as a whole;translatemay also be a callable such thattranslate(callback, value)translatesvalueby usingcallback(term)to retrieve the translation of terms.
-
class
odoo.fields.Selection(selection=<object object>, string=<object object>, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
odoo.fields.Field- Parameters
selection – specifies the possible values for this field. It is given as either a list of pairs (
value,string), or a model method, or a method name.selection_add – provides an extension of the selection in the case of an overridden field. It is a list of pairs (
value,string).
The attribute
selectionis mandatory except in the case of related fields or field extensions.
Date and Datetime fields¶
Dates and Datetimes are very important fields in any kind of business application, they are heavily used in many popular Odoo applications such as logistics or accounting and their misuse can create invisible yet painful bugs, this excerpt aims to provide Odoo developers with the knowledge required to avoid misusing these fields.
- When assigning a value to a Date/Datetime field, the following options are valid:
A string in the proper server format (YYYY-MM-DD) for Date fields, (YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS) for Datetime fields.
A
dateordatetimeobject.FalseorNone.
If not sure of the type of the value being assigned to a Date/Datetime object,
the best course of action is to pass the value to
to_date() or to_datetime()
which will attempt to convert the value to a date or datetime object
respectively, which can then be assigned to the field in question.
Example
To parse date/datetimes coming from external sources:
fields.Date.to_date(self._context.get('date_from'))
- Date / Datetime comparison best practices:
Date fields can only be compared to date objects.
Datetime fields can only be compared to datetime objects.
Warning
Strings representing dates and datetimes can be compared between each other, however the result may not be the expected result, as a datetime string will always be greater than a date string, therefore this practice is heavily discouraged.
Common operations with dates and datetimes such as addition, subtraction or
fetching the start/end of a period are exposed through both
Date and Datetime.
These helpers are also available by importing odoo.tools.date_utils.
-
class
odoo.fields.Date(string=<object object>, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
odoo.fields.Field-
static
add(value, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Return the sum of
valueand arelativedelta.- Parameters
value – initial date or datetime.
args – positional args to pass directly to
relativedelta.kwargs – keyword args to pass directly to
relativedelta.
- Returns
the resulting date/datetime.
-
static
context_today(record, timestamp=None)[source]¶ Return the current date as seen in the client’s timezone in a format fit for date fields. This method may be used to compute default values.
- Parameters
record – recordset from which the timezone will be obtained.
timestamp (datetime) – optional datetime value to use instead of the current date and time (must be a datetime, regular dates can’t be converted between timezones).
- Return type
date
-
static
end_of(value, granularity)[source]¶ Get end of a time period from a date or a datetime.
- Parameters
value – initial date or datetime.
granularity – Type of period in string, can be year, quarter, month, week, day or hour.
- Returns
A date/datetime object corresponding to the start of the specified period.
-
static
start_of(value, granularity)[source]¶ Get start of a time period from a date or a datetime.
- Parameters
value – initial date or datetime.
granularity – type of period in string, can be year, quarter, month, week, day or hour.
- Returns
a date/datetime object corresponding to the start of the specified period.
-
static
subtract(value, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Return the difference between
valueand arelativedelta.- Parameters
value – initial date or datetime.
args – positional args to pass directly to
relativedelta.kwargs – keyword args to pass directly to
relativedelta.
- Returns
the resulting date/datetime.
-
static
to_date(value)[source]¶ Attempt to convert
valueto adateobject.- This function can take as input different kinds of types:
A falsy object, in which case None will be returned.
A string representing a date or datetime.
A date object, in which case the object will be returned as-is.
A datetime object, in which case it will be converted to a date object and all datetime-specific information will be lost (HMS, TZ, …).
- Parameters
value – value to convert.
- Returns
an object representing
value.- Return type
date
-
static
-
class
odoo.fields.Datetime(string=<object object>, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
odoo.fields.Field-
static
add(value, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Return the sum of
valueand arelativedelta.- Parameters
value – initial date or datetime.
args – positional args to pass directly to
relativedelta.kwargs – keyword args to pass directly to
relativedelta.
- Returns
the resulting date/datetime.
-
static
context_timestamp(record, timestamp)[source]¶ Returns the given timestamp converted to the client’s timezone. This method is not meant for use as a default initializer, because datetime fields are automatically converted upon display on client side. For default values,
fields.Datetime.now()should be used instead.- Parameters
record – recordset from which the timezone will be obtained.
timestamp (datetime) – naive datetime value (expressed in UTC) to be converted to the client timezone.
- Return type
datetime
- Returns
timestamp converted to timezone-aware datetime in context timezone.
-
static
end_of(value, granularity)[source]¶ Get end of a time period from a date or a datetime.
- Parameters
value – initial date or datetime.
granularity – Type of period in string, can be year, quarter, month, week, day or hour.
- Returns
A date/datetime object corresponding to the start of the specified period.
-
static
now(*args)[source]¶ Return the current day and time in the format expected by the ORM. This function may be used to compute default values.
-
static
start_of(value, granularity)[source]¶ Get start of a time period from a date or a datetime.
- Parameters
value – initial date or datetime.
granularity – type of period in string, can be year, quarter, month, week, day or hour.
- Returns
a date/datetime object corresponding to the start of the specified period.
-
static
subtract(value, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Return the difference between
valueand arelativedelta.- Parameters
value – initial date or datetime.
args – positional args to pass directly to
relativedelta.kwargs – keyword args to pass directly to
relativedelta.
- Returns
the resulting date/datetime.
-
static
to_datetime(value)[source]¶ Convert an ORM
valueinto adatetimevalue.- This function can take as input different kinds of types:
A falsy object, in which case None will be returned.
A string representing a date or datetime.
A datetime object, in which case the object will be returned as-is.
A date object, in which case it will be converted to a datetime object.
- Parameters
value – value to convert.
- Returns
an object representing
value.- Return type
datetime
-
static
Relational fields¶
-
class
odoo.fields.Many2one(comodel_name=<object object>, string=<object object>, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
odoo.fields._RelationalThe value of such a field is a recordset of size 0 (no record) or 1 (a single record).
- Parameters
comodel_name – name of the target model (string)
domain – an optional domain to set on candidate values on the client side (domain or string)
context – an optional context to use on the client side when handling that field (dictionary)
ondelete – what to do when the referred record is deleted; possible values are:
'set null','restrict','cascade'auto_join – whether JOINs are generated upon search through that field (boolean, by default
False)delegate – set it to
Trueto make fields of the target model accessible from the current model (corresponds to_inherits)
The attribute
comodel_nameis mandatory except in the case of related fields or field extensions.
-
class
odoo.fields.One2many(comodel_name=<object object>, inverse_name=<object object>, string=<object object>, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
odoo.fields._RelationalMultiOne2many field; the value of such a field is the recordset of all the records in
comodel_namesuch that the fieldinverse_nameis equal to the current record.- Parameters
comodel_name – name of the target model (string)
inverse_name – name of the inverse
Many2onefield incomodel_name(string)domain – an optional domain to set on candidate values on the client side (domain or string)
context – an optional context to use on the client side when handling that field (dictionary)
auto_join – whether JOINs are generated upon search through that field (boolean, by default
False)limit – optional limit to use upon read (integer)
The attributes
comodel_nameandinverse_nameare mandatory except in the case of related fields or field extensions.
-
class
odoo.fields.Many2many(comodel_name=<object object>, relation=<object object>, column1=<object object>, column2=<object object>, string=<object object>, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
odoo.fields._RelationalMultiMany2many field; the value of such a field is the recordset.
- Parameters
comodel_name – name of the target model (string)
The attribute
comodel_nameis mandatory except in the case of related fields or field extensions.- Parameters
relation – optional name of the table that stores the relation in the database (string)
column1 – optional name of the column referring to “these” records in the table
relation(string)column2 – optional name of the column referring to “those” records in the table
relation(string)
The attributes
relation,column1andcolumn2are optional. If not given, names are automatically generated from model names, providedmodel_nameandcomodel_nameare different!- Parameters
domain – an optional domain to set on candidate values on the client side (domain or string)
context – an optional context to use on the client side when handling that field (dictionary)
limit – optional limit to use upon read (integer)
-
class
odoo.fields.Reference(selection=<object object>, string=<object object>, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
odoo.fields.Selection
Inheritance and extension¶
Odoo provides three different mechanisms to extend models in a modular way:
creating a new model from an existing one, adding new information to the copy but leaving the original module as-is
extending models defined in other modules in-place, replacing the previous version
delegating some of the model’s fields to records it contains
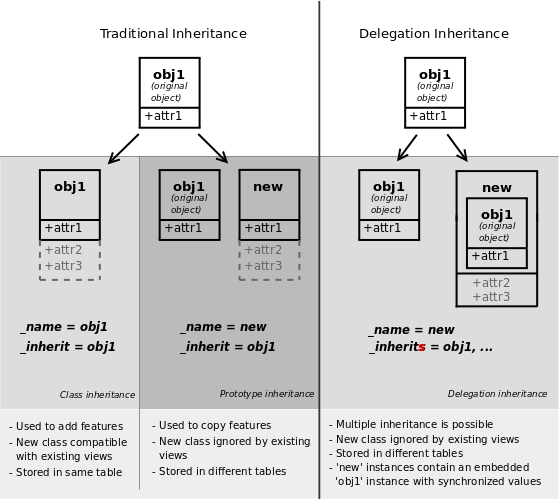
Classical inheritance¶
When using the _inherit and
_name attributes together, Odoo creates a new
model using the existing one (provided via
_inherit) as a base. The new model gets all the
fields, methods and meta-information (defaults & al) from its base.
class Inheritance0(models.Model):
_name = 'inheritance.0'
_description = 'Inheritance Zero'
name = fields.Char()
def call(self):
return self.check("model 0")
def check(self, s):
return "This is {} record {}".format(s, self.name)
class Inheritance1(models.Model):
_name = 'inheritance.1'
_inherit = 'inheritance.0'
_description = 'Inheritance One'
def call(self):
return self.check("model 1")
and using them:
a = env['inheritance.0'].create({'name': 'A'})
b = env['inheritance.1'].create({'name': 'B'})
a.call()
b.call()
will yield:
"This is model 0 record A"
"This is model 1 record B"
the second model has inherited from the first model’s check method and its
name field, but overridden the call method, as when using standard
Python inheritance.
Extension¶
When using _inherit but leaving out
_name, the new model replaces the existing one,
essentially extending it in-place. This is useful to add new fields or methods
to existing models (created in other modules), or to customize or reconfigure
them (e.g. to change their default sort order):
class Extension0(models.Model):
_name = 'extension.0'
_description = 'Extension zero'
name = fields.Char(default="A")
class Extension1(models.Model):
_inherit = 'extension.0'
description = fields.Char(default="Extended")
record = env['extension.0'].create({})
record.read()[0]
will yield:
{'name': "A", 'description': "Extended"}
Delegation¶
The third inheritance mechanism provides more flexibility (it can be altered
at runtime) but less power: using the _inherits
a model delegates the lookup of any field not found on the current model
to “children” models. The delegation is performed via
Reference fields automatically set up on the parent
model.
The main difference is in the meaning. When using Delegation, the model has one instead of is one, turning the relationship in a composition instead of inheritance:
class Screen(models.Model):
_name = 'delegation.screen'
_description = 'Screen'
size = fields.Float(string='Screen Size in inches')
class Keyboard(models.Model):
_name = 'delegation.keyboard'
_description = 'Keyboard'
layout = fields.Char(string='Layout')
class Laptop(models.Model):
_name = 'delegation.laptop'
_description = 'Laptop'
_inherits = {
'delegation.screen': 'screen_id',
'delegation.keyboard': 'keyboard_id',
}
name = fields.Char(string='Name')
maker = fields.Char(string='Maker')
# a Laptop has a screen
screen_id = fields.Many2one('delegation.screen', required=True, ondelete="cascade")
# a Laptop has a keyboard
keyboard_id = fields.Many2one('delegation.keyboard', required=True, ondelete="cascade")
record = env['delegation.laptop'].create({
'screen_id': env['delegation.screen'].create({'size': 13.0}).id,
'keyboard_id': env['delegation.keyboard'].create({'layout': 'QWERTY'}).id,
})
record.size
record.layout
will result in:
13.0
'QWERTY'
and it’s possible to write directly on the delegated field:
record.write({'size': 14.0})
Warning
when using delegation inheritance, methods are not inherited, only fields
Warning
_inheritsis more or less implemented, avoid it if you can;chained
_inheritsis essentially not implemented, we cannot guarantee anything on the final behavior.
Domains¶
A domain is a list of criteria, each criterion being a triple (either a
list or a tuple) of (field_name, operator, value) where:
field_name(str)a field name of the current model, or a relationship traversal through a
Many2oneusing dot-notation e.g.'street'or'partner_id.country'operator(str)an operator used to compare the
field_namewith thevalue. Valid operators are:=equals to
!=not equals to
>greater than
>=greater than or equal to
<less than
<=less than or equal to
=?unset or equals to (returns true if
valueis eitherNoneorFalse, otherwise behaves like=)=likematches
field_nameagainst thevaluepattern. An underscore_in the pattern stands for (matches) any single character; a percent sign%matches any string of zero or more characters.likematches
field_nameagainst the%value%pattern. Similar to=likebut wrapsvaluewith ‘%’ before matchingnot likedoesn’t match against the
%value%patternilikecase insensitive
likenot ilikecase insensitive
not like=ilikecase insensitive
=likeinis equal to any of the items from
value,valueshould be a list of itemsnot inis unequal to all of the items from
valuechild_ofis a child (descendant) of a
valuerecord.Takes the semantics of the model into account (i.e following the relationship field named by
_parent_name).parent_ofis a parent (ascendant) of a
valuerecord.Takes the semantics of the model into account (i.e following the relationship field named by
_parent_name).
valuevariable type, must be comparable (through
operator) to the named field
Domain criteria can be combined using logical operators in prefix form:
'&'logical AND, default operation to combine criteria following one another. Arity 2 (uses the next 2 criteria or combinations).
'|'logical OR, arity 2.
'!'logical NOT, arity 1.
Tip
Mostly to negate combinations of criteria
Individual criterion generally have a negative form (e.g.
=->!=,<->>=) which is simpler than negating the positive.
Example
To search for partners named ABC, from belgium or germany, whose language is not english:
[('name','=','ABC'),
('language.code','!=','en_US'),
'|',('country_id.code','=','be'),
('country_id.code','=','de')]
This domain is interpreted as:
(name is 'ABC')
AND (language is NOT english)
AND (country is Belgium OR Germany)
Porting from the old API to the new API¶
bare lists of ids are to be avoided in the new API, use recordsets instead
methods still written in the old API should be automatically bridged by the ORM, no need to switch to the old API, just call them as if they were a new API method. See Automatic bridging of old API methods for more details.
search()returns a recordset, no point in e.g. browsing its resultfields.relatedandfields.functionare replaced by using a normal field type with either arelated=or acompute=parameterdepends()oncompute=methods must be complete, it must list all the fields and sub-fields which the compute method uses. It is better to have too many dependencies (will recompute the field in cases where that is not needed) than not enough (will forget to recompute the field and then values will be incorrect)remove all
onchangemethods on computed fields. Computed fields are automatically re-computed when one of their dependencies is changed, and that is used to auto-generateonchangeby the clientthe decorators
model()andmulti()are for bridging when calling from the old API context, for internal or pure new-api (e.g. compute) they are uselessremove
_default, replace bydefault=parameter on corresponding fieldsif a field’s
string=is the titlecased version of the field name:name = fields.Char(string="Name")
it is useless and should be removed
the
multi=parameter does not do anything on new API fields use the samecompute=methods on all relevant fields for the same resultprovide
compute=,inverse=andsearch=methods by name (as a string), this makes them overridable (removes the need for an intermediate “trampoline” function)double check that all fields and methods have different names, there is no warning in case of collision (because Python handles it before Odoo sees anything)
the normal new-api import is
from odoo import fields, models. If compatibility decorators are necessary, usefrom odoo import api, fields, modelsavoid the
one()decorator, it probably does not do what you expectremove explicit definition of
create_uid,create_date,write_uidandwrite_datefields: they are now created as regular “legitimate” fields, and can be read and written like any other field out-of-the-boxwhen straight conversion is impossible (semantics can not be bridged) or the “old API” version is not desirable and could be improved for the new API, it is possible to use completely different “old API” and “new API” implementations for the same method name using
v7()andv8(). The method should first be defined using the old-API style and decorated withv7(), it should then be re-defined using the exact same name but the new-API style and decorated withv8(). Calls from an old-API context will be dispatched to the first implementation and calls from a new-API context will be dispatched to the second implementation. One implementation can call (and frequently does) call the other by switching context.Danger
using these decorators makes methods extremely difficult to override and harder to understand and document
uses of
_columnsor_all_columnsshould be replaced by_fields, which provides access to instances of new-styleodoo.fields.Fieldinstances (rather than old-styleodoo.osv.fields._column).Non-stored computed fields created using the new API style are not available in
_columnsand can only be inspected through_fieldsreassigning
selfin a method is probably unnecessary and may break translation introspectionEnvironmentobjects rely on some threadlocal state, which has to be set up before using them. It is necessary to do so using theodoo.api.Environment.manage()context manager when trying to use the new API in contexts where it hasn’t been set up yet, such as new threads or a Python interactive environment:>>> from odoo import api, modules >>> r = modules.registry.RegistryManager.get('test') >>> cr = r.cursor() >>> env = api.Environment(cr, 1, {}) Traceback (most recent call last): ... AttributeError: environments >>> with api.Environment.manage(): ... env = api.Environment(cr, 1, {}) ... print env['res.partner'].browse(1) ... res.partner(1,)
Automatic bridging of old API methods¶
When models are initialized, all methods are automatically scanned and bridged if they look like models declared in the old API style. This bridging makes them transparently callable from new-API-style methods.
Methods are matched as “old-API style” if their second positional parameter
(after self) is called either cr or cursor. The system also
recognizes the third positional parameter being called uid or user and
the fourth being called id or ids. It also recognizes the presence of
any parameter called context.
When calling such methods from a new API context, the system will
automatically fill matched parameters from the current
Environment (for cr,
user and
context) or the current recordset (for id
and ids).
In the rare cases where it is necessary, the bridging can be customized by decorating the old-style method:
disabling it entirely, by decorating a method with
noguess()there will be no bridging and methods will be called the exact same way from the new and old API stylesdefining the bridge explicitly, this is mostly for methods which are matched incorrectly (because parameters are named in unexpected ways):
cr()will automatically prepend the current cursor to explicitly provided parameters, positionally
cr_uid()will automatically prepend the current cursor and user’s id to explicitly provided parameters
cr_uid_ids()will automatically prepend the current cursor, user’s id and recordset’s ids to explicitly provided parameters
cr_uid_id()will loop over the current recordset and call the method once for each record, prepending the current cursor, user’s id and record’s id to explicitly provided parameters.
Danger
the result of this wrapper is always a list when calling from a new-API context
All of these methods have a
_context-suffixed version (e.g.cr_uid_context()) which also passes the current context by keyword.dual implementations using
v7()andv8()will be ignored as they provide their own “bridging”