AI server actions¶
AI server actions extend Odoo’s automation framework by allowing artificial intelligence to make decisions during a workflow.
They are designed for cases where logic cannot be expressed entirely through fixed conditions, but still requires controlled execution through standard server actions.
How AI server actions work¶
AI-driven workflows in Odoo are built around a clear separation of responsibilities between the AI server action, or the Manager, and the tool, or the Worker.
AI server action: the manager¶
An AI server action acts as a decision maker, or a manager. It reads the record and its context. It interprets the AI prompt. And it decides which tool to call, and what arguments to use.
The server action does not enforce business rules, modify records directly, or guarantee the correctness of the operation. Its role is limited to decision-making.
AI tool: the worker¶
A tool is a standard server action with the Use in AI option enabled in its Usage tab. Tools contain all execution logic and perform record updates, moves, or writes. Tools must enforce business rules explicitly in Python code.
If a tool is called by the AI server action, it will execute unconditionally, unless the code itself prevents it.
AI server action workflow¶
The AI server action workflow follows this sequence:
A record triggers an AI server action.
The AI prompt is evaluated, using the record as context.
The AI selects one of the available tools.
The AI provides arguments expected by the tool.
The selected tool executes its Python code.
Important
AI server actions work without custom logic only when the underlying behavior already exists in Odoo, such as moving a document to a folder. In these cases, the AI selects parameters, and Odoo executes the action.
Use case walkthrough¶
The Auto-sort documents in Inbox example demonstrates the full AI Server Action pattern. Navigate to the Server Actions menu by going to .
Note
This server action is designed to review documents for their content, and add tags. The action itself does not move documents or add tags, it only decides which tool should be used, based on the documents’ content.
The Model for the action is listed as Document, and the Type is AI.
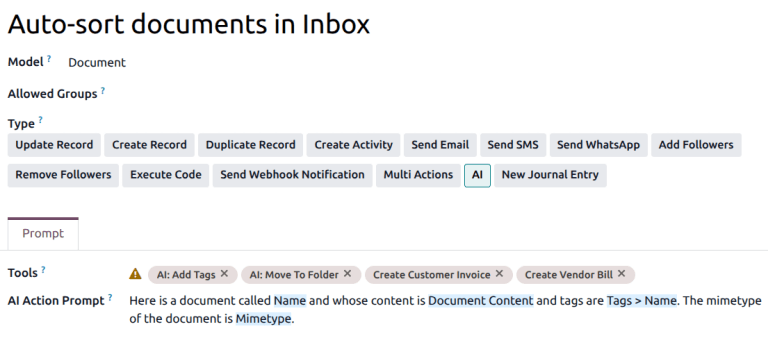
The prompt for this action provides context about the document, as well as intent of the action.
The Tool field includes several actions that may be taken based on this prompt, including moving a document, adding tags, or creating invoices or bills.
Note
AI: Add Tags, AI: Move to Folder, and AI: Rename Document are all Execute Code server actions, meaning they trigger python code.
For example, if the action determines, based on the content of the document, that the most appropriate tool is AI: Move to Folder, the Python code performs the following operation:
ai['result'] = record._ai_action_move_in_folder(folder_id)
This code, executes unconditionally when called and performs the move using an existing method.
Note
The AI does not infer arguments from the Python code or from the method signature. Instead, arguments passed to a tool are determined entirely by the tool’s configuration.
For the AI: Move to Folder tool, the Python code expects a variable named folder_id. The AI
knows to provide folder_id because it is explicitly declared as an argument in the
configuration. This can be found on the Usage tab of the server action, in the AI
Schema field. The Name column under AI Schema must match the variable name used in
the Python code exactly.
The AI uses the argument description to understand what the parameter represents, what type of value is expected, and when it is appropriate to supply it.
If an argument is not defined in the Usage tab, the AI cannot provide it, even if the Python code references it.

Creating custom AI tools¶
The same pattern in the Auto-sort documents in Inbox example above can be implemented using standard Odoo logic. For example, to create an action that can update a task description, an Execute Code action could be created with the following code:
record.write({'description': content})
To function correctly, content must be defined as an argument in tool’s Usage tab.
See also
Common issues¶
Why is the Tools field empty?¶
Confirm that at least one server action has Use in AI enabled.
Confirm that at least one tool is assigned to the same model Model as the server action.
Why did the tool run but nothing happened?¶
The Python code exited without changes.
Required arguments were missing or empty.
Business conditions were not implemented in the tool logic.
Why did the AI choose an unexpected tool?¶
The prompt lacked sufficient context.
Multiple tools matched the same intent.
No constraints were enforced at the tool level.